Scalable. Secure. Built for What’s Next.
Every successful business today runs on technology. But here’s the thing: not every IT setup is designed to keep up with your growth. Outdated servers, scattered data, security loopholes — they don’t just slow you down, they hold you back.
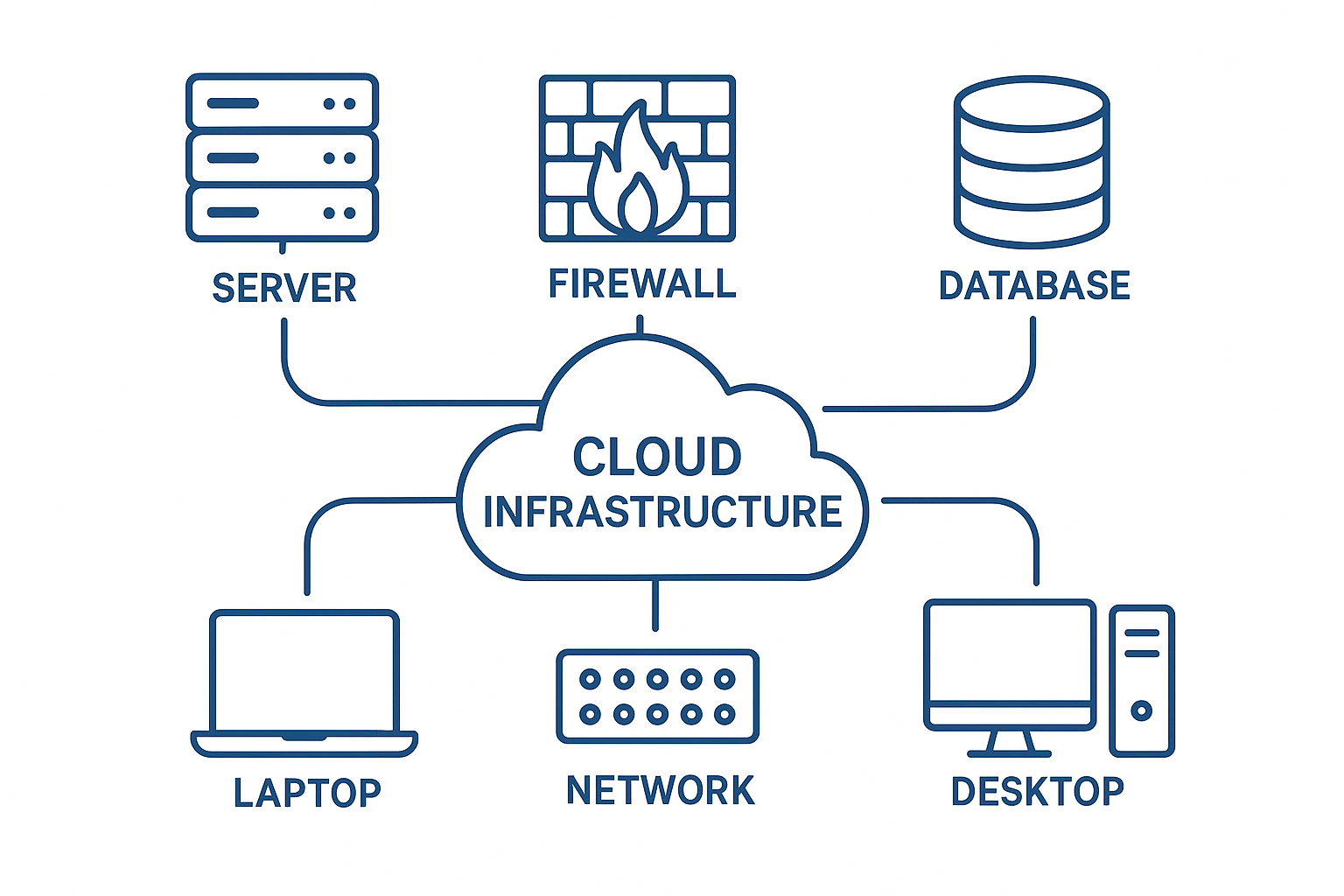
That’s where Mentor Infocomm comes in. We help you build a foundation that’s not just strong for today, but ready for tomorrow. With our IT infrastructure services in India, cloud migration services, and IT infrastructure management in Chennai, we give you a system that adapts, protects, and scales with your vision.
Think of us as the architects of your digital backbone — designing environments where downtime is prevented, data stays safe, and your team can focus on growth instead of firefighting IT issues.
Cloud, On Your Terms
The cloud isn’t a single path — it’s a choice. And the right choice depends on your industry, your data, and your ambitions. That’s why we give you options:
Public Cloud (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud)
- Instant Scalability – Whether it’s exam season or a retail sale, systems scale seamlessly to handle demand.
- Global Reach – With servers worldwide, latency drops and experience improves everywhere.
- High Availability – Built-in redundancy and multi-data center reliability even during crises.
Private Cloud / On-Premise
- Data Sovereignty – For finance, government, healthcare — ensures compliance and local control.
- Tailored Fit – Private infrastructure integrates seamlessly with your systems and policies.
Hybrid Cloud Solutions
- Best of Both Worlds – Keep critical workloads on-site; use public cloud for flexibility and overflow.
- Balanced Efficiency – Sensitive where it matters, flexible where it counts.
That’s why more organizations today are choosing hybrid cloud solutions with us — power of public + safety of private, without compromise.
Smarter Infrastructure, Better Performance
Shifting to the cloud isn’t the end goal. Making it work harder for you is.
That’s why we use cloud-native technologies to maximize performance and lower costs:
- Containers (Docker, Kubernetes) – Apps packaged once, run anywhere — consistent, portable, error-free.
- Serverless Computing (AWS Lambda, Azure Functions) – Only pay for what you use. Scale instantly and save costs.
- GPU Clusters – High-performance computing for AI, analytics, or machine learning tasks.
The result? Lower costs, faster deployments, and systems that never feel sluggish.
Data That Drives Decisions
Your data isn’t just information — it’s insight. And in the right hands, it can guide smarter business moves.
That’s why we build data ecosystems that are reliable, scalable, and built for growth:
- Scalable Object Storage – Keep everything from CCTV footage to customer call logs safe and affordable.
- Data Lakes – Unified pools for structured and unstructured data, ready for analytics.
- Relational & Non-Relational Databases – Data organized, accessible, and actionable.
With our cloud backup services in India, your data is not just stored — it’s protected and ready to power growth.
Security You Can Trust
A chain is only as strong as its weakest link. At Mentor Infocomm, security is never an afterthought — it’s designed into every layer:
- End-to-End Encryption – Protecting your data at rest and in motion.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) – Ensuring only the right eyes see the right data.
- Continuous Monitoring – Automated 24/7 vigilance for unusual activity.
- Threat Detection & Quick Response – Identifying risks before they escalate.
- Global Compliance Standards – Certified for GDPR, HIPAA, SOC2 — enabling global expansion.
With Mentor Infocomm’s cybersecurity services in India, you get more than protection. You get confidence.
Why Partner With Us?
We don’t just deliver IT — we deliver peace of mind. With 24/7 IT monitoring, remote support, and outsourced IT management, we stay with you beyond deployment — ensuring your systems run smoothly, your people stay productive, and your business stays ahead.
Ready to build the IT foundation your business deserves?
Let’s talk.







 Call Now
Call Now