What is Cloud Computing? A Beginner’s Guide to the Future of IT
Welcome to the Cloud: Unlocking Digital Potential
In today`s fast-paced digital world, businesses and individuals are constantly seeking innovative ways to store, manage, and process data. Cloud computing has emerged as a transformative technology, revolutionizing how we interact with technology. This website will guide you through the essentials of cloud computing, its advantages, and the major players driving this revolution.
What is Cloud Computing? (The Basics)
At its core, cloud computing is the delivery of on-demand computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet ("the cloud"). Instead of owning and maintaining your own computing infrastructure, you can access these services from a cloud provider, paying only for what you use.
Think of it like electricity: you don`t generate your own power; you simply plug into the grid and pay for the electricity you consume. Cloud computing works similarly, allowing you to "plug into" vast computing resources without the upfront investment and ongoing maintenance of physical hardware.
Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing:
- On-Demand Self-Service: Users can provision computing capabilities, such as server time and network storage, as needed, automatically without requiring human interaction with each service provider.
- Broad Network Access: Capabilities are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms that promote use by heterogeneous thin or thick client platforms (e.g., mobile phones, laptops, and tablets).
- Resource Pooling: The provider`s computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers using a multi-tenant model, with different physical and virtual resources dynamically assigned and reassigned according to consumer demand.
- Rapid Elasticity: Capabilities can be elastically provisioned and released to scale rapidly outward and inward commensurate with demand. To the consumer, the capabilities available for provisioning often appear to be unlimited and can be appropriated in any quantity at any time.
- Measured Service: Cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource usage by leveraging a metering capability at some level of abstraction appropriate to the type of service (e.g., storage, processing, bandwidth, and active user accounts). Resource usage can be monitored, controlled, and reported, providing transparency for both the provider and consumer of the utilized service.
Service Models:
Cloud computing typically offers three main service models:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides fundamental computing resources like virtual machines, storage, networks, and operating systems. You manage the operating system, applications, and data, while the cloud provider manages the underlying infrastructure. Examples: Amazon EC2, Azure Virtual Machines, Google Compute Engine.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform that allows developers to build, run, and manage applications without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure typically associated with developing and launching an app. Examples: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Azure App Service, Google App Engine.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users access the software via a web browser or mobile app, and the cloud provider manages all aspects of the application, from infrastructure to maintenance. Examples: Google Workspace (Gmail, Docs), Salesforce, Microsoft 365.
Deployment Models:
Cloud services can also be deployed in different ways:
- Public Cloud: Services are delivered over the public internet and shared among multiple organizations.
- Private Cloud: Cloud infrastructure is operated exclusively for a single organization, either managed internally or by a third party.
- Hybrid Cloud: A combination of public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This offers greater flexibility and more deployment options.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing offers a multitude of advantages for businesses of all sizes:
- Cost Savings: Reduce capital expenditure by eliminating the need to purchase expensive hardware and software. Pay-as-you-go models mean you only pay for the resources you consume.
- Scalability and Elasticity: Easily scale resources up or down to meet fluctuating demands, ensuring optimal performance without over-provisioning or under-provisioning.
- Increased Agility and Innovation: Rapidly deploy new applications and services, experiment with new technologies, and bring products to market faster.
- Global Reach: Deploy applications and data in multiple geographic regions, reducing latency for users worldwide and improving disaster recovery capabilities.
- Reliability and High Availability: Cloud providers offer robust infrastructure with built-in redundancy and disaster recovery mechanisms, ensuring high uptime for your applications.
- Enhanced Security: Reputable cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, often offering more robust protection than individual organizations can achieve on-premises. They implement advanced security features, regular updates, and compliance certifications.
- Improved Collaboration: Cloud-based tools and storage facilitate seamless collaboration among teams, regardless of their geographical location.
- Reduced IT Burden: Offload infrastructure management, maintenance, and updates to the cloud provider, allowing your IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
Leading Cloud Providers: AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure
The cloud computing market is dominated by a few major players, each with its unique strengths and offerings.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Overview: AWS is the most mature and widely adopted cloud platform, offering an extensive array of services (over 200). It has the largest global footprint and a vast ecosystem of partners and tools.
- Key Strengths:
- Comprehensive Service Catalog: Offers the broadest and deepest set of services across compute, storage, databases, networking, analytics, machine learning, IoT, and more.
- Market Leader: Holds the largest market share, indicating its maturity and reliability.
- Flexibility: Provides highly customizable environments, giving users granular control over their infrastructure.
- Common Services:
- EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud): Scalable virtual servers.
- S3 (Simple Storage Service): Object storage for data lakes, backups, and archives.
- RDS (Relational Database Service): Managed relational databases.
- Lambda: Serverless compute service for running code without provisioning servers.
- VPC (Virtual Private Cloud): Isolated virtual networks.
Microsoft Azure
- Overview: Azure is Microsoft`s cloud platform, known for its strong integration with Microsoft enterprise products and its focus on hybrid cloud solutions. It`s a strong choice for businesses already heavily invested in Microsoft technologies.
- Key Strengths:
- Hybrid Cloud Capabilities: Excellent for organizations that need to integrate their on-premises infrastructure with cloud resources.
- Microsoft Ecosystem Integration: Seamless integration with Windows Server, Active Directory, SQL Server, and other Microsoft products.
- Enterprise Focus: Tailored for large enterprises, offering robust security and compliance features.
- Common Services:
- Azure Virtual Machines: Scalable virtual machines.
- Azure Storage: Various storage options (blob, file, disk).
- Azure SQL Database: Managed relational database service.
- Azure App Service: Platform for building, deploying, and scaling web apps.
- Azure Active Directory (Entra ID): Identity and access management.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Overview: Google Cloud leverages Google`s expertise in data management, analytics, and machine learning. It`s known for its competitive pricing, strong open-source support (especially Kubernetes), and advanced AI/ML capabilities.
- Key Strengths:
- Data Analytics and Machine Learning: Industry-leading services for big data processing, analytics, and AI/ML.
- Open Source and Kubernetes: Strong support for open-source technologies, particularly Kubernetes (Google developed Kubernetes).
- Global Network Infrastructure: Leverages Google`s high-performance global network.
- Competitive Pricing: Often offers competitive pricing, especially for sustained usage.
- Common Services:
- Google Compute Engine: Scalable virtual machines.
- Google Cloud Storage: Object storage with various classes.
- Cloud SQL: Managed relational database service.
- Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE): Managed Kubernetes service.
- BigQuery: Serverless, highly scalable enterprise data warehouse.
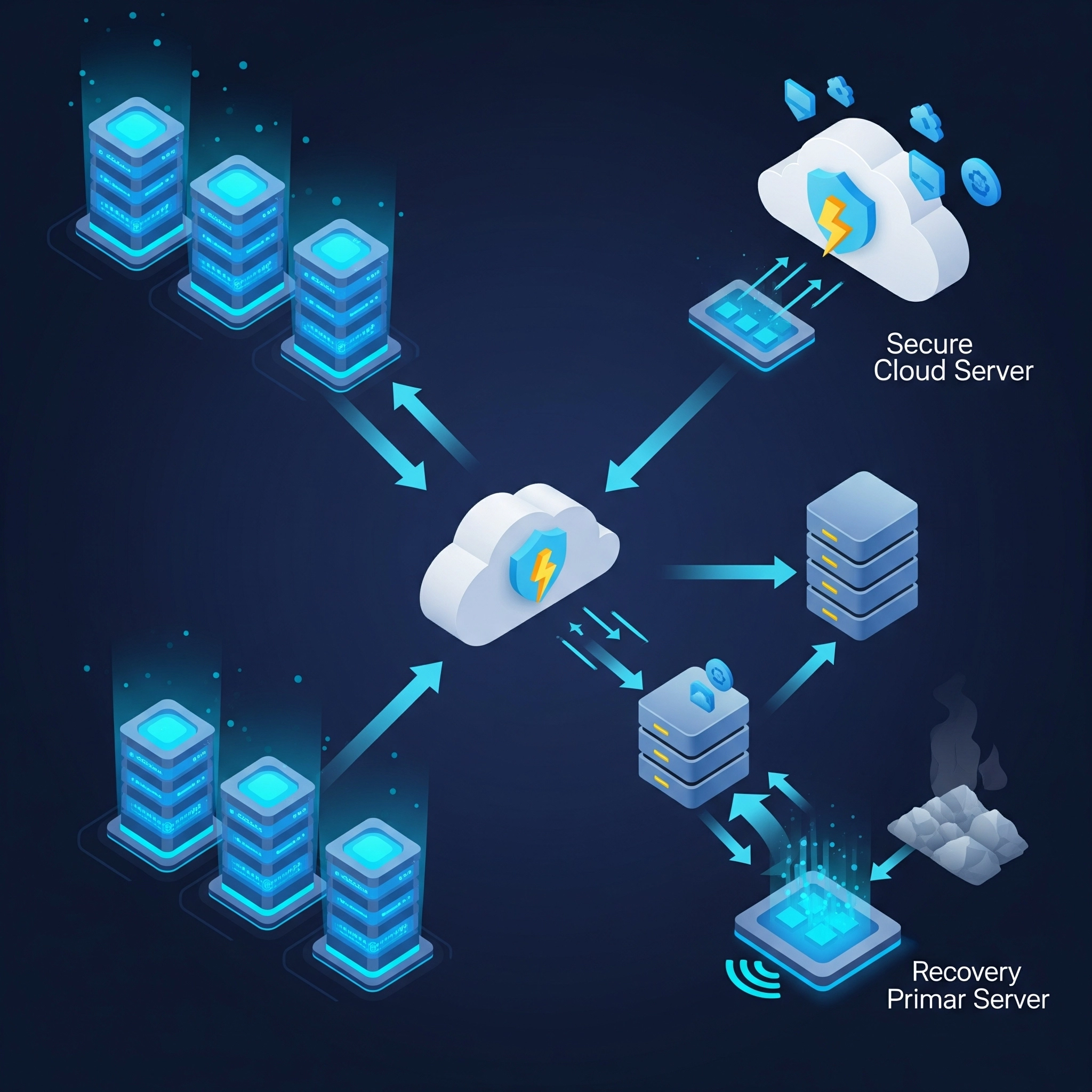
Cloud Security: A Shared Responsibility
Cloud security is a paramount concern for any organization adopting cloud computing. It`s crucial to understand the shared responsibility model:
- Cloud Provider`s Responsibility (Security of the Cloud): The cloud provider is responsible for the security of the underlying infrastructure, including the physical facilities, network, hardware, and the virtualization layer.
- Customer`s Responsibility (Security in the Cloud): The customer is responsible for securing their data, applications, operating systems, network configurations, and access controls within the cloud environment. This includes identity and access management (IAM), data encryption, network security rules, and application security.
Best Practices for Cloud Security:
- Understand the Shared Responsibility Model: Clearly define what your cloud provider secures and what you are responsible for.
- Implement Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM): Use multi-factor authentication (MFA), enforce the principle of least privilege, and regularly review user permissions.
- Encrypt Data: Encrypt data at rest (storage) and in transit (network communication).
- Configure Network Security: Implement virtual private clouds (VPCs), subnets, security groups, and network access control lists (ACLs) to control traffic flow.
- Regularly Monitor and Log: Utilize cloud provider monitoring tools and centralized logging to detect and respond to security incidents promptly.
- Patch and Update Regularly: Ensure operating systems, applications, and any installed software are kept up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Proactively identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in your cloud environment.
- Develop an Incident Response Plan: Prepare for potential security breaches with a clear plan for detection, containment, eradication, and recovery.
- Security Awareness Training: Educate your employees about cloud security risks and best practices.
Get Started with Cloud Computing
Embracing cloud computing can transform your business by enhancing agility, reducing costs, and fostering innovation. Whether you`re a startup looking for scalable infrastructure or an enterprise seeking to modernize your IT, the cloud offers a powerful solution. Explore the free tiers and trials offered by AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure to start your cloud journey today!







 Call Now
Call Now